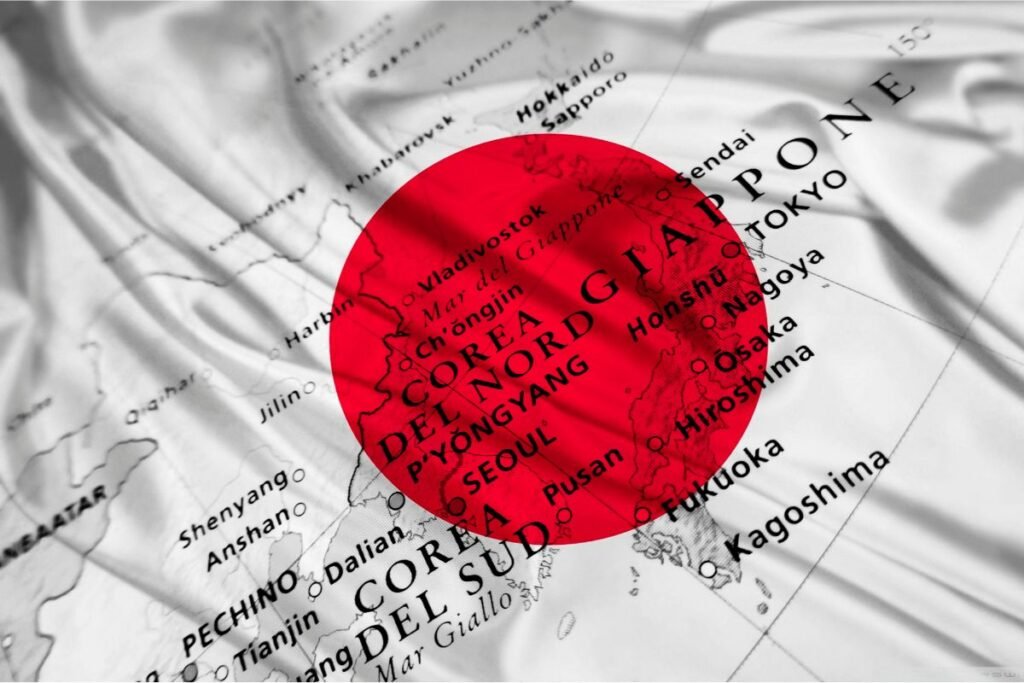
Japan is a country, actually an island, in the continent of Asia. Japan is actually part of ‘the Ring of Fire’, an archipelago of 6852 separate islands.
Many of which are under Japanese rule, but with particular interest in the four larger islands of Hokkaido, Shikoku, and Kyushu, as well as smaller islands that are considered part of Japan as a country.
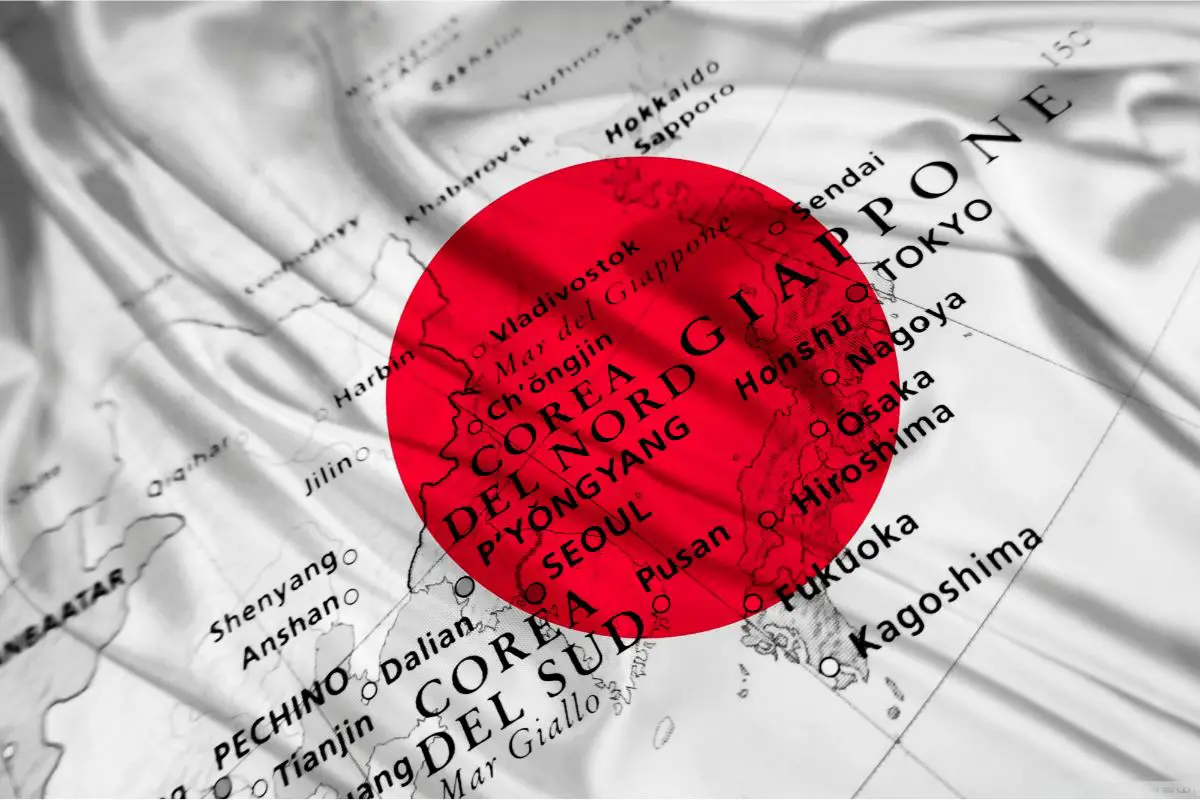
What is considered Japanese territory is all within what is regarded as East Asia, east of the Eurasian Continent.
Japan’s easternmost point is Minami-Tori Shima Island, its westernmost point is Yonaguni Jima Island, with its southernmost tip in Oki-no-Tori Shima Island and its northernmost tip in Etorofu Island.
Japan’s largest island, Honshu, is 228,000 square meters and is the seventh largest island in the world.
Japan is a very highly developed country, being the 11th most populated country in the world, as well as being one of the most urbanized.
Most of its population are forced into cities with around three fourths of the island’s geography being mountainous so most of the population, with most cities being somewhat coastal as a response.
Since the 1970s with the technological revolution Japan has been a large power within the world, with many conglomerate companies.
With this economic success Japan became internationally renowned as people got wind of its unique culture and cuisine, both which are now a mainstay in the US and internationally.
The position of the Japanese archipelago in terms of the equator, and the seas it is surrounded by, have a large effect on the country’s geography and secondarily on their culture and day-to-day life.
By looking at the ocean Japan is located in, or pecans, we can learn more about Japan as a country.
Japan’s Geographical Position And It’s Consequences
Japan is an archipelago, which refers to a cluster or string of islands often under one sovereign rule, that comprises around 6852 islands on the Pacific coast of Asia. As a result Japan has one of the longest coastlines of any country.
As it is on the Pacific coast of Asia we can generally attribute Japan to the Pacific Ocean, but this single answer does not really indulge the geographic position of Japan in detail.
Japan’s archipelago stretches over 3000 km so you can imagine it might have coastline with more than one sea. The Japanese archipelago is surrounded by the Pacific Ocean, but borders the Sea of Okhotsk, the Sea of Japan, and the East China Sea.
It’s important to note that geographically a sea is a smaller part of an ocean. Lake Biwa is the largest freshwater lake in the country as well, considered an ‘ancient lake’ it has carried water for more than one million years, some researchers suggest potentially 2.6 million years.
The country of Japan is located right on the Pacific Ring of Fire, a colloquially geographical term that refers to the areas around the pacific that are specifically vulnerable to natural disasters as a result.
It’s outline is very much around the countries that share a coast with the Pacific Ocean.
As a result of this position near the pacific, Japan has become an area at large risk of earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions.
The danger of these natural disasters was all too apparent in 2011 when a 15 meter tsunami disable the power supply of three nuclear reactors at the Fukushima nuclear plant, causing a nuclear incident in the country.
Japan has the 17th highest natural disaster risk, measured in 2016, as a result of its geographical position. The land of the rising sun is also home to 111 active volcanoes, if any of them went off there could be huge disasters as a result.
In 1923 the historic earthquake in Tokyo killed over 140,000 people. Other notable disasters are the Great Hanshin earthquake in 1995 with around 6,500 deaths, and even as recent as the Tohoku earthquake which caused the tsunami that led to the Fukushima disaster.
This earthquake was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan, and the fourth most powerful in the world since record keeping began.
If infrastructure, and modern architecture, had not changed since the 1923 earthquake, which was much weaker than the 2011 earthquake, it would be likely that more would have died.
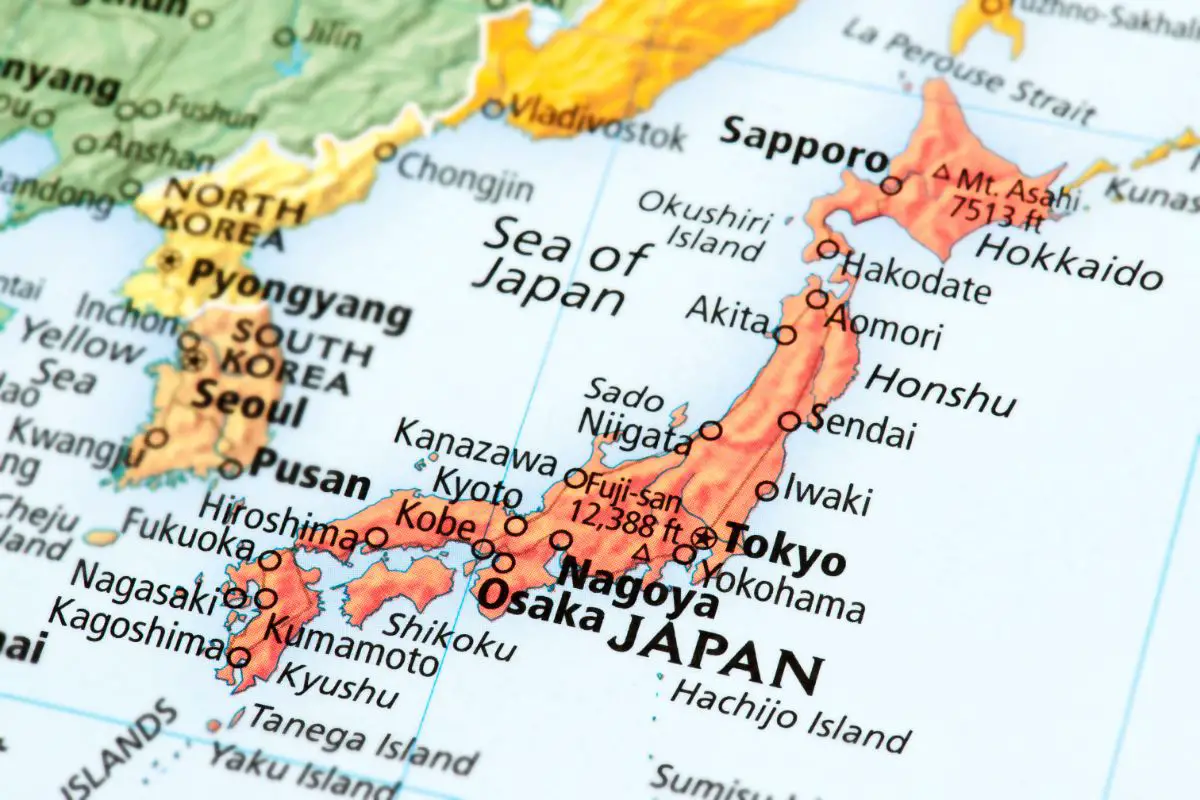
Climate
One large result of Japan’s position within the Pacific Ocean is its varied and interesting climate.
While the southern regions of Ryukyu and Bonin islands are subtropical forests, Hokkaido in the north of Japan can often exhibit some of the largest snowfall in the Country, with the city of Sapporo seeing on average around 191 inches of snow each year.
On the West coast of Honshu, the Sea of Japan brings a northwest wind that also brings heavy snowfall in the winter, although can experience very dry and hot spells thanks to a ‘foehn’, a geographical term, which is a downslope wind.
Many other areas of Japan are heavily affected by the winds their coastal sea carries, which are often not always hot like we would assume of the Pacific Ocean.
Final Thoughts
What should be clear is that Japan is located in the Pacific Ocean.
Along with its various seas that hug Japan’s record-making long coastline, the winds and temperatures that the archipelago are subject to can lead to some very varied climate on the island from some of the highest snowfall in the world in Hokkaido, so the subtropical region of Ryukyu.
One effect of this varied climate, as well as its location within the Pacific’s Ring of Fire, make Japan an extremely at-high-risk island for natural disasters.
While deaths caused by natural disasters have waned in the country thanks to better infrastructure and architectural protection, there have been some record deaths caused by earthquakes in this country.